The BRICS bloc—comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa—is set to expand in 2024 by adding new member countries from Africa, Asia, and Latin America. This expansion aims to strengthen economic cooperation among emerging markets and reduce dependence on the U.S. dollar in global trade. By exploring alternative financial systems, including a BRICS-backed digital currency, the bloc hopes to reshape the global financial landscape. However, these ambitions face significant challenges, including resistance from established economies and uncertainties in currency adoption.
As BRICS expands its influence, it marks a significant shift toward a more multipolar world order, where emerging economies play an increasingly pivotal role in global finance and governance.
Source: Statista
BRICS vs. G7: Shifting Economic Power
BRICS has increasingly extended its influence across developing nations, according to Statista. This expansion highlights the bloc’s growing strategic importance in the Global South, as it seeks to enhance economic cooperation and provide an alternative to traditional Western-led institutions.
Based on World Bank data, in 2023, BRICS accounted for 35.7% of global GDP, surpassing the G7, which saw a decline to 29.9%. This surge in economic influence has attracted interest from other nations, including Malaysia and Thailand, which have expressed interest in joining BRICS to diversify their international alliances and reduce dependence on traditional Western-dominated institutions.
Ongoing Efforts to Challenge Dollar Dominance
Over the past few years, BRICS countries have taken several steps to reduce their reliance on the U.S. dollar, a cornerstone of their broader strategy to enhance economic sovereignty.
The De-Dollarization of China’s Cross-Border Transactions:
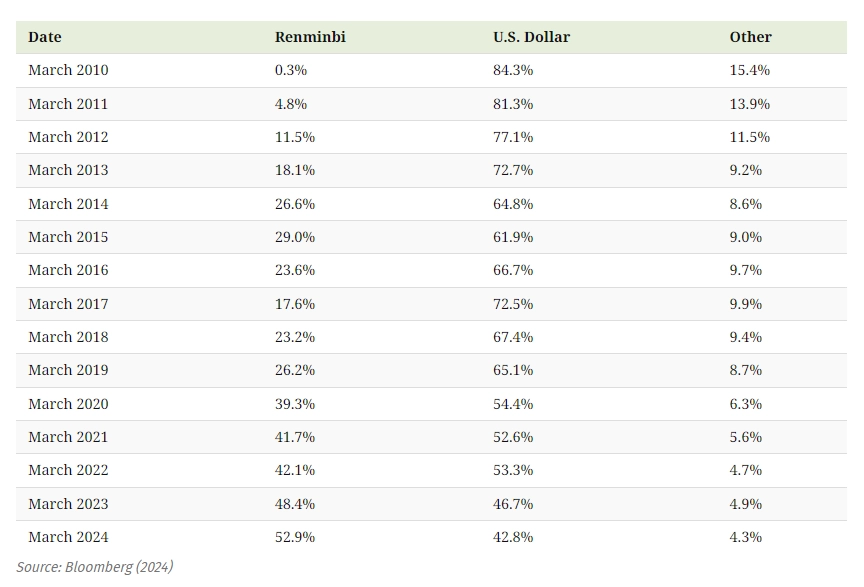
China and Russia have progressively shifted towards trading in local currencies, particularly in the energy sector. According to Bloomberg, in March 2023, the share of the RMB in China’s settlements surpassed the USD for the first time. As of March 2024, over half (52.9%) of Chinese payments were settled in RMB while 42.8% were settled in USD. This is double the share from five years previous.
India’s Trade Diversification:
India has expanded its trade with Russia, notably increasing oil imports, and has explored payment mechanisms in rupees to avoid sanctions and reduce dollar dependency. This aligns with India’s broader strategy of enhancing economic sovereignty, though it has drawn international scrutiny.
Brazil-China Bilateral Agreements:
Brazil has negotiated bilateral agreements with China to settle trade in their respective currencies. This initiative is part of Brazil’s broader efforts to deepen ties with BRICS members and reduce exposure to dollar volatility.
South Africa’s Intra-BRICS Trade:
South Africa has focused on strengthening intra-BRICS trade, particularly in minerals and commodities, to benefit from diversified trade routes and currency options.
Developing New Financial Infrastructure
BRICS members are actively working on creating new financial infrastructure to support their economic goals:
The New Development Bank (NDB), formerly BRICS Development Bank:
Established in 2014, the NDB has financed various infrastructure and sustainable development projects across member countries. By providing funding in local currencies, the NDB seeks to reduce reliance on Western financial institutions and the dollar.
Digital Currencies and Payment Systems:
Discussions are underway to develop a BRICS-backed digital currency that could facilitate trade within the bloc. Additionally, members are exploring blockchain-based payment systems that bypass the SWIFT network, which is heavily dominated by Western countries.
Challenges in Establishing a New Financial Order
The effort to reduce dollar dependence is ambitious but comes with significant hurdles. The U.S. dollar is deeply entrenched in global finance, offering stability and liquidity that many countries rely on. A BRICS-backed digital currency could provide an alternative, potentially backed by local currencies or gold. However, gaining widespread adoption and trust in this new currency will be challenging, especially in regions with strong ties to Western financial systems.
The dollar’s appeal as a safe haven currency adds further complexity. While BRICS aims to create a more multipolar financial system, the transition away from the dollar is likely to be gradual, with associated risks for businesses and investors engaged in international markets.
Opportunities and Risks for Businesses and Investors
The expansion of BRICS presents a mix of opportunities and risks for businesses and investors. Companies operating within BRICS countries could benefit from increased trade and reduced transaction costs through new financial instruments.
Opportunities:
Energy Stability: Companies trading in local currencies may experience greater stability, reducing exposure to dollar volatility.
Diversified Trade Routes: South Africa’s focus on intra-BRICS trade offers diversified routes and reduced dependency on Western markets.
Risks:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Evolving regulatory frameworks and the success of new financial infrastructure pose risks.
Political Sensitivities: Sectors like finance and technology could face complications due to political sensitivities and differing regulatory environments.
Conclusion: Navigating a Shifting Global Landscape
The BRICS expansion marks a significant development in the evolving landscape of global finance and trade. While the bloc’s efforts to create alternative financial systems and reduce dollar dependence hold promise, they also present substantial challenges and uncertainties. As the global economic order becomes increasingly multipolar, the success of BRICS’ ambitions will depend on the bloc’s ability to build trust, foster cooperation, and deliver tangible benefits to its member nations and the broader global community.
In this shifting landscape, businesses and investors must carefully navigate the opportunities and risks, remaining vigilant as the dynamics of global finance continue to evolve.
What’s Next? Looking ahead, the upcoming BRICS summit will likely focus on finalizing the digital currency initiative and solidifying the new members’ integration. Businesses should monitor these developments closely, as they will have far-reaching implications for global trade and finance.
Disclaimer:
The content provided in this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, legal, or investment advice. The insights shared are based on current information and analysis, and they do not necessarily reflect the official stance of the institution on these matters. Readers are encouraged to conduct their own research and consult with a professional advisor before making any financial decisions.






